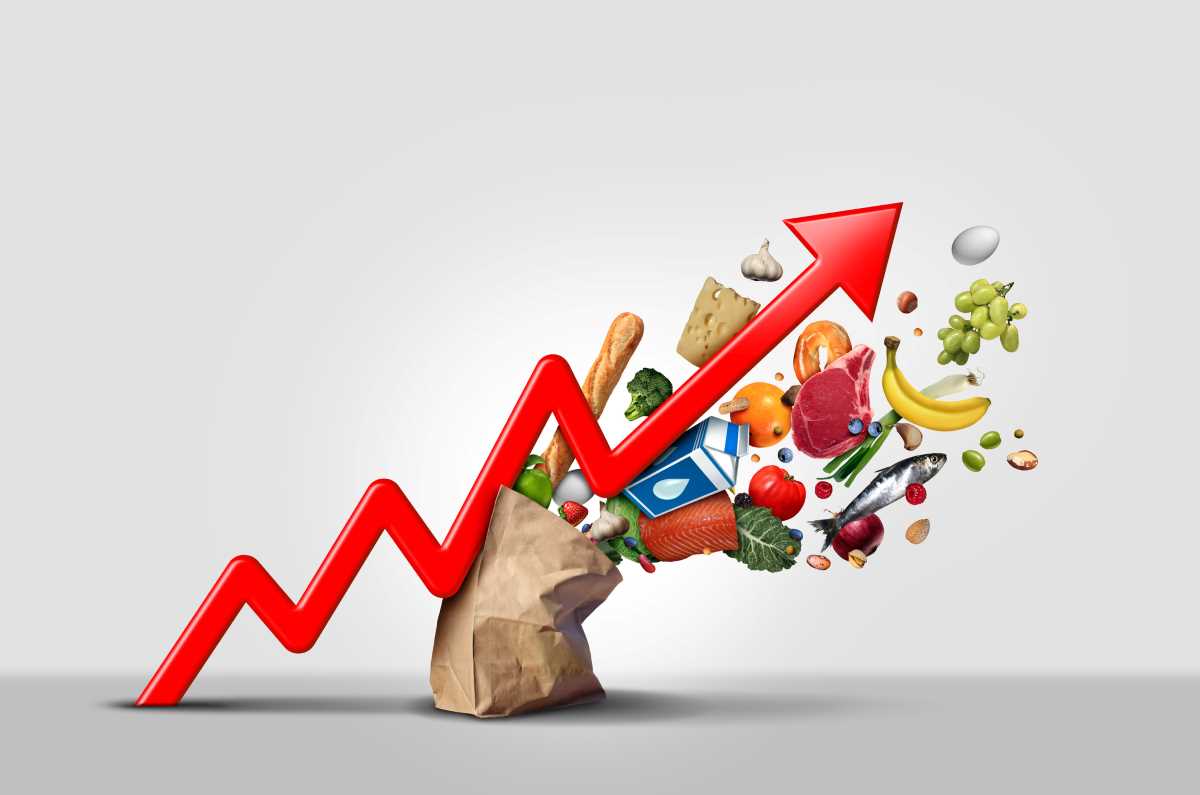
Times are tough; there’s no denying that. The rising costs of everything (hello, $10 iceberg lettuce 😭) are putting the household budget under significant pressure. And this is causing many of us to feel anxious.
But we can do many practical things to relieve some of this stress. Let’s start in the kitchen with our tips for enjoying tasty, healthy meals and snacks that won’t cost an arm and a leg.
Make a meal plan – and stick to it
Before hitting the shops, plan your meals and snacks for the week. Check the fridge and pantry to see what ingredients you already have, and write a list of those you need. Writing a list is essential because, even if you’re not in pain or dealing with brain fog, it’s easy to forget things, buy the wrong quantities or items you don’t need in the heat of the moment. (Step away from the chips Lisa 😁). And if, like me, you hate shopping and really want to avoid crowds and germs, getting the shopping done quickly and efficiently is a must. With the steep price of petrol, it also makes sense to keep the trips to the shops to a minimum. So plan, plan, plan! Eatforhealth.gov.au has some helpful information on meal planning, including sample mean plans. There are also lots of meal planning apps you can download from Google Play or the App Store. They conveniently place your meal plan and shopping list on your phone, so no more forgotten shopping lists!
It’s a good habit to get into so you can track the amount of energy (kilojoules), fat, salt, sugar etc., in your foods. It’s also helpful when comparing different brands of the same product.
Swap some meat dishes for vegetarian or vegan meals
Research has found that vegan and vegetarian diets cost less than a diet that includes meat. You don’t have to go all-out vego; simply swap some of your meat dishes for plant-based meals. They’re tasty, healthy and cheap. Healthy vegetarian protein sources include tofu, chickpeas, beans, quinoa, lentils, eggs and nuts. If you need help, there are many websites with interesting and tasty vegetarian and vegan recipes.
Note: You’ve probably noticed the multitude of plant-based ‘meats’ crowding the shelves in your supermarket, often alongside actual meat products. They’ve been developed to look and taste like meat and can be a good alternative to meat, especially if your family aren’t keen on giving tofu a go 😉! Just make sure you read the nutritional panel carefully before buying these products, as some have high levels of salt, saturated fat and other additives. The Cleveland Clinic has an interesting article to help you know what to look for when buying faux meats.
Choose generic, home brand and no-name products
They’re generally cheaper and are often exactly the same as the name brand, just without the fancy packaging.
Prepare some meals in advance
When you’ve got some free time, make extra meals that you can freeze and use when necessary. That way, when you’re exhausted, having a flare, or just can’t be bothered cooking, you’ll have some meals you know are healthy. And you won’t have to resort to takeaway foods or store-bought frozen meals, which can be costly and are often high in fat, salt and/or sugar.
Buy local and in-season fruit and veg
They’re generally more nutritious, fresher and more cost-effective. The Australian Farmers’ Markets Association has a tool to help you find your local farmers’ market, and Sustainable Table has a handy seasonal produce guide.
Buy so-called ‘ugly’ produce
These fruits and vegetables are cheaper and taste fine. Who cares if your carrot has two ‘legs’ or your apple has a spot? At the end of the day, they’re perfectly healthy and packed with all the usual nutrients. They just don’t look shiny and new, but who does these days 😉? You can get imperfect produce at many supermarkets and food subscription services.
Read the unit price when comparing products
This will enable you to see the price difference regardless of brand or quantity, and you can work out which provides the best value for money. Unit pricing works by using a standard measurement across all products of the same type.
So, for example, if you compared yoghurt A with yoghurt B:
- yoghurt A costs $6.40 for 1kg, so its unit price is $0.64 per 100g
- yoghurt B costs $2.30 for 200g, so its unit price is $1.15 per 100g.
That makes yoghurt A cheaper per 100g.
Fortunately, you don’t have to do the mental gymnastics to work this out for yourself. The unit price is generally provided on the shelf label and online. Phew! Shopping is hard enough!
Grow your own
Over the past few years, many of us have discovered the joy of gardening. So why not grow some of your own produce? Whether on a small scale with a few pots of herbs on your balcony or larger scale vegie patch and fruit trees in your backyard, you can experience the pleasure and reap the rewards of growing some of your own foods. Nothing tastes sweeter than the food you’ve nurtured, grown and picked yourself 💚.
Use frozen and canned fruit and vegetables
They’re still healthy and usually cheaper than produce that’s not in season. They’ll also keep longer. Just make sure you read the ingredients list and nutrition panel. Canned foods may have added salt or sugar. So for vegies, look for ‘no added salt’ on the label, and choose fruits in natural juice with no added sugar rather than canned in syrup.
Shop around and do your research
Just because you’ve always shopped at a particular place doesn’t mean you always have to shop there. Visit the local farmer’s markets, keep an eye on catalogues and join online groups with other savvy shoppers. That way, you’ll always know who’s providing the best value for money for your groceries.
Buy in bulk items you use regularly and have a long shelf life
This includes things like rice, dried/canned legumes and pasta. And the best time to buy them is when they’re on sale. But please don’t go crazy and start hoarding or buying too much 😐. Bulk buying to save money is different to the panic buying we’ve seen during the pandemic. If we all shop for only the things we need, there’ll be plenty for everyone.
Reduce your kitchen waste
Shopping with a list will help, and only buy what you need. Take note of the foods you often throw out because they’ve become a mysterious, furry blob in your fridge. Avoid buying that item, or buy less of it when you shop. Look for ways to use food that’s becoming slightly less than fresh but is still good. Soups are a great way to use the last of the vegies in your fridge crisper. Visit the Foodwise website for tips to help you reduce waste.
Getting takeaway
Let’s face it, there’ll be times when you really, really want takeaway food. It’s quick, easy and delicious 😋. As long as it’s an occasional thing and you eat it in moderation, it shouldn’t have too great an impact on your health or wallet. Here are some tips from Health and Wellbeing Queensland to help you make the healthiest choices when it comes to takeaway food.
Finally, don’t shop when you’re hungry
It’s an easy way to end up with lots of things in your trolley that weren’t on your shopping list. This can blow your budget and plans for healthy eating right out of the water. So shop after you’ve eaten or munch on some fruit or handful of nuts before you even consider walking into the bright lights and air-conditioned aisles of your local shopping centre. Your budget will thank you for it.
Contact our free national Helpline
Call our friendly team if you have questions about managing your pain, musculoskeletal condition, treatment options, mental health issues, telehealth, or accessing services. They’re available weekdays between 9am-5pm on 1800 263 265; email (helpline@muscha.org) or via Messenger.
More to explore